Back-to-Back-Testing: What is that?
The back-to-back test, like the regression test, is a dynamic software test procedure and describes a test execution method in which two variants of a software are compared with each other. One variant is the test object and the other variant is the reference. In back-to-back testing, the reference is the basis for the automated evaluation used to decide whether a test case is considered successful or failed.
The variants of this execution methodology can be divided into two basic types:
- Changes to a software without a change in the execution platform, e.g. C code is extended with new functionalities, bug fixes are performed or the software structure is rebuilt (refactoring).
- Changes to a software for a change of the execution platform – in most cases new files are generated, e.g. when translating a Simulink or Targetlink model into C-code by means of automatic code generation or compilation of C-code for a target processor architecture.
The basic goal of a back-to-back test is to detect the effects of software changes. This involves comparing the behavior of a changed software against another variant of the software in order to uncover errors in the implementation or generation.
Recommendation for the selection of references in back-to-back testing
It is very important that a reference in back-to-back testing is trustworthy because it is the source of truth and therefore the basis for all evaluations of the test run in back-to-back testing. Trust can be established through testing, reviews, trial or, in some exceptional cases, experience and monitoring in a production environment (“proven-in-use” approach).
A successful back-to-back test means equality between the variants of a software.
A statement regarding compliance with requirements and functionality is only valid if this statement already applies to the reference and back-to-back testing has been performed with full stimulation. Insufficient stimulation can lead to errors or hidden functionalities not being detected in the reference or in the SUT.
We therefore recommend measuring the code coverage for both the reference and the SUT during back-to-back testing.
The Modified Condition Decision Coverage (MC/DC) is one of the strictest code coverage metrics and therefore very well suited for back-to-back testing. Sufficient coverage is acceptable with a value of 100% MC/DC.
Test cases not yet available for achieving 100% code coverage (MC/DC) can also be generated for a back-to-back test. The test cases do not have to be significant in terms of requirements or functionality, since the expected value is specified by the reference.
Typical application areas of back-to-back testing are:
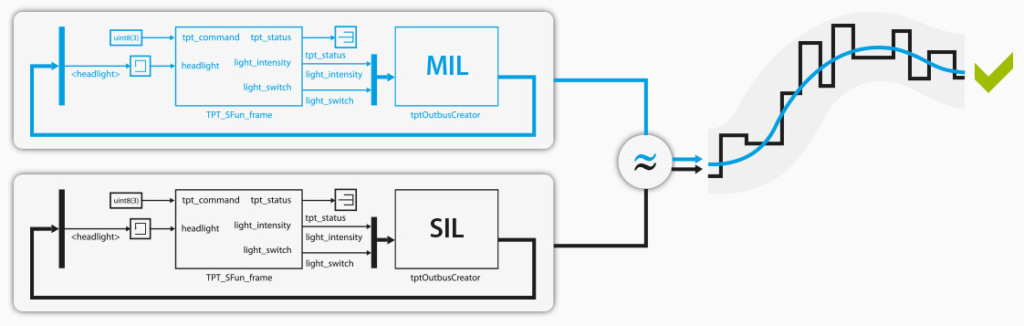
- Comparison of model (MiL) and software code (SiL): testing whether software exhibits the same behavior as the model. Concrete examples
-
- Simulink model vs. Autosar SW component (watch the video)
- Targetlink model vs. generated software
- Models vs. hand-coded software
- Comparison of model (MiL) and target software (PiL): check whether the software on target architecture and processor show the same behavior as the model.
- Comparison of software (SiL) and target software (PiL): check whether the software on the target architecture and processor exhibit the same behavior as the software on the host.
- Comparison of software in different versions: testing whether a version exhibits the same behavior as a previous version (testing of refactoring measures).
- Comparison in relation to a reference test run (MiL/SiL): Checking whether the behavior corresponds to a validated test run, e.g. in the case of complex control loops.
Requirement of the use of back-to-back tests in standards/standards:
The international automotive safety standard ISO 26262 recommends the use of back-to-back testing for highly safety critical functions, such as ASIL C and ASIL D, in software unit and software integration verification between code and models.
How is back-to-back testing possible in TPT?
Back-to-back testing is very easy to set up in TPT. It can be executed with a few simple steps. The methodology is available for all levels (unit test, integration test up to product level) and platforms. You can reuse the test cases from previous tests in back-to-back testing or create test cases with our test generator at the push of a button. Using our co-simulation platform FUSION any connections can be made independently and easily.
How to set up a back-to-back test in TPT from scratch can be seen in our video Back-to-Back Testing of AUTOSAR vs. MATLAB Model.
After the test execution, a test report is automatically generated. This report contains:
- all signal characteristics of all inputs and outputs of your SUT, as well as all measured values
- auxiliary signals for an easier analysis of deviations
- an evaluation of the behavior of your SUT based on all signals with configurable tolerances.
All test results are stored in TPT. So the behavior can be analyzed and traced in the Signal Viewer of TPT at any time.
A test case is always considered successful if the behavior of the SUT compared to the reference is identical within the tolerances for selected inputs and outputs.
The tolerances of signals can be defined globally for a test execution. This is useful if, for example, deviations in floating point calculations are expected.