
CI/CT & Cloud Testing
In TPT, many activities in the testing process can be automated. The grade of automation of functionalities matters a lot in automation.
A programmable API that can be used for automation. In addition, other supporting functions and modules are available to help users automate large parts of the testing process – always with the overall goal: finding bugs faster.
TPT covers the full scope of automation in all test processes: from the connection of the system under test, the test case creation, the test execution, the evaluation, up to the reporting. There are hardly any limits to automation in TPT.
TPT runs in the cloud and can be integrated into Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Testing (CT) environments. Users can create and execute their own scripts for complex or repeatable tasks.
The use cases of our customers are versatile. TPT allows for all possibilities.
Cloud Testing
There are many reasons to test in the cloud instead of on the local machine.
Technologically, TPT can be integrated into a Docker container or into a virtual machine. The basis is an operating system in the environment. Currently, Windows and Linux are supported.
Depending on the setup, different use cases are possible, such as.
- Parallel execution of tests to reduce test execution time
- Archiving and recovery of test environment (bug fixes)
- Avoiding long downloads when test data and tools are in the cloud
This type of implementation allows hosting at different cloud providers (Microsoft Azure, Amazon AWS, IBM Cloud, … ).
Continuous Integration / Continuous Testing (CI/CT)
The basic goal of Continuous Integration and Continuous Testing (CI/CT) is to find out as soon as possible if a change in the code base leads to problems in the final product. In other words: finding bugs early.
In most cases the journey goes like this:
A developer changes the code base and enters the code into a version control system (like Git or Subversion). The so-called commit is recorded by the CI system and the code change goes through several Quality Gates before it is included in the main branch of the product. Part of the Quality Gates is a dynamic testing of the change. In the first step, unit tests are run. If these are successful, SW integration tests are triggered by the CI environment. The system knows the dependent structures from unit to overall integration for the entire product. If a test fails in the cascade, the change is not propagated to the main path. The level and the failed test are visualized to the user. As a result, the code is adjusted again.
This approach is established in agile projects and in DevOps. The main advantage is that the developer still remembers the changes to the code due to the prompt feedback. The effort required to familiarize oneself with the context of a change is usually eliminated. This in turn has a positive effect on productivity.
TPT as a test automation solution can be integrated into different CI/CT environments. For the widely used automation server Jenkins, we have developed a plugin that runs test in master-slave or standalone and provides the test results in Jenkins.
The connection of further CI environments can be done via the TPT API or via Command Line Options.
API
Using the cloud for test execution or CI/CT, the highest level of automation must be reached. The most common approach is to use tools with Application Programming Interfaces (API). An API allows access to a package of functions and procedures of a program. This access allows operating systems, applications or other services to control the program and exchange data with it.
TPT received its first API with Release 3. This has been continuously extended with further functions and procedures in subsequent releases. TPT has three programmable APIs with different purposes and application areas.
- the Virtual Machine API (VM API)
- the Fusion API
- the TPT API
In addition, controlling TPT via the command line is also possible.
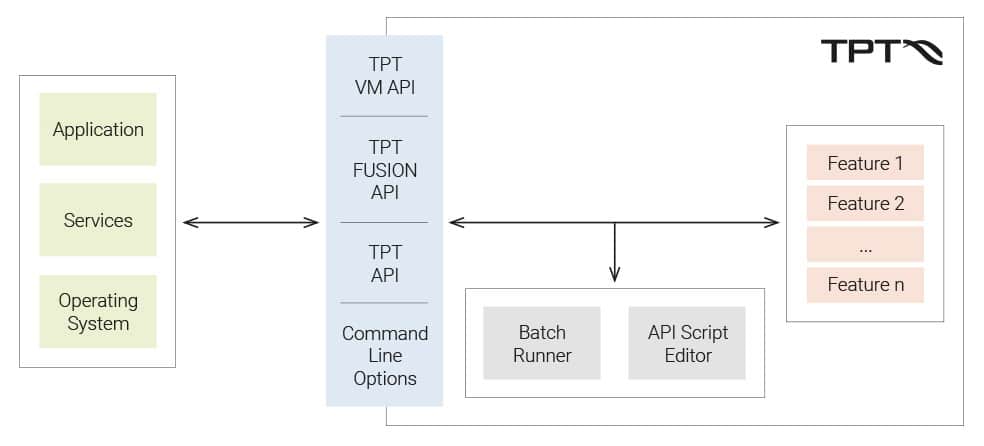
Figure 1: Overview of the interaction with internal and external services, applications and Operating Systems
The TPT VM API is used to connect a System under Test (SUT) to our TPT VM, the test execution engine of TPT. The TPT VM is based on C and provides methods for initialization, interfacing, test execution steps, termination etc. The TPT-VM API can be used to interface almost any kind of SUT as long as you can access it via C/C++.
The TPT FUSION API is analogous to TPT VM API and is used when you want to connect any SUT or stimulation element to our co-simulation platform FUSION. You can connect any number and all kinds of technologies. Thus, you can build any test environment constructs in the mix and use them for testing. Whether real hardware, software, application, models or any combination: TPT knows no limits when building the test environment.
The TPT API is used to implement various functions of TPT in other programs. We divide the TPT API into two areas:
- JAVA API
- Python bindings
The Java API of TPT is used to create your own programs and to control TPT remotely. With TPT comes a complete documentation, an Eclipse project and several examples to illustrate the programming.
Python bindings provide access to the full range of the Java TPT API. They can be used in API scripts or directly in TPT projects.
TPT scripts can be created in our two Editors:
- the Batch Runner
- the API Script Editor
Both editors also allow manual execution of the created scripts. The script behavior can thus be observed in TPT – automation is thus easier and problems are detected earlier.
The Batch Runner is primarily intended as support for the user (Level 1). The programming is done by intuitive step sequences. It supports automation of test executions, reports and can update test harnesses (e.g. in case of updated SUTs).
The ability to run saved scripts from the API script editor allows even non-expert TPT users to run sophisticated scripts in a simple and understandable way.
Our API Script Editor is a development environment that is integrated in TPT. It can be used for the complete automation of sub-processes in the test process including more than test design and test execution and supports the Python and Java programming languages.
Once created, the automation scripts can be saved, loaded and thus reused in other projects or teams.
The Command Line Options allow access via the console of an Operating System (OS). With command line you can load projects, generate test frames, execute tests, and much more. The interface to the Command Line Options is documented in detail in our User Guide. The command line options can also be used to execute scripts.
The wide range of supported TPT functions allows extensive automation and nearly 85% of TPT’s GUI functionalities.
Related topics
Test Environments
You can test with TPT in multiple test environments from MiL, SiL, PiL, HiL to automated driving tests.

ADAS/AD Testing
TPT is ideally suited for testing Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) at any test level.

TPT Testing Tool
With TPT, you can test ECU software and embedded control systems in all development phases from MiL, SiL, PiL, HiL, ECU testing to vehicle testing.